Theme
Our research focuses on epigenetic dynamics during mammalian germ cell development and fertilization. Epigenetic inheritance from arents to progeny has been catching a huge attention, thus our research can contribute to elucidate the mechanism.
About Research
Epigenetics : Supporting proper transgenerational transmission of genetic information
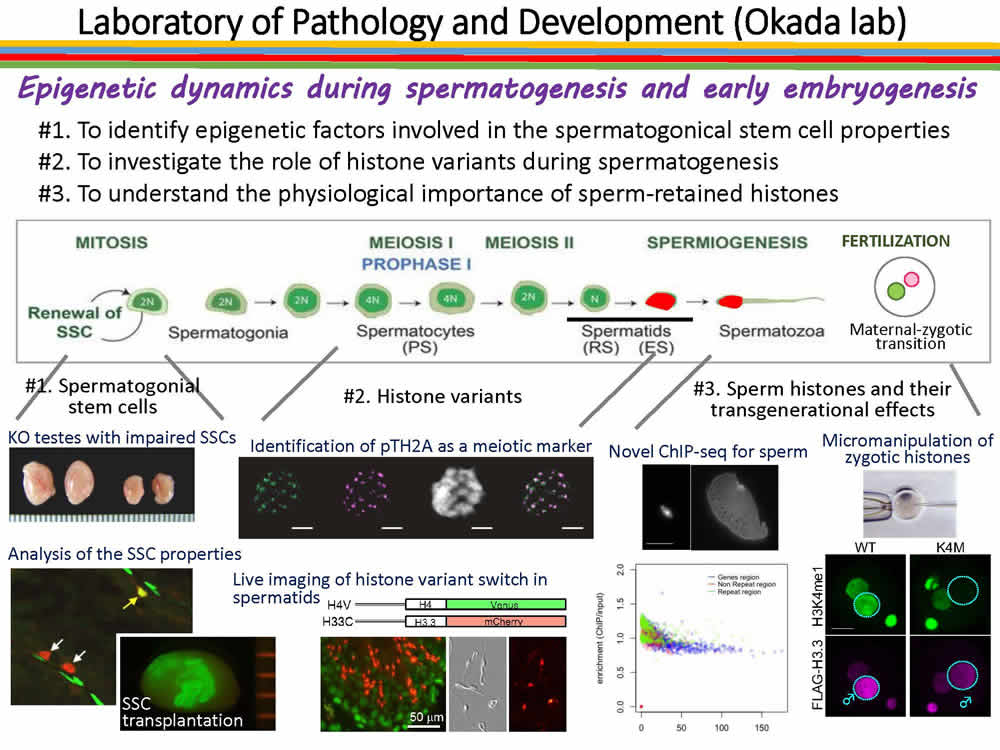
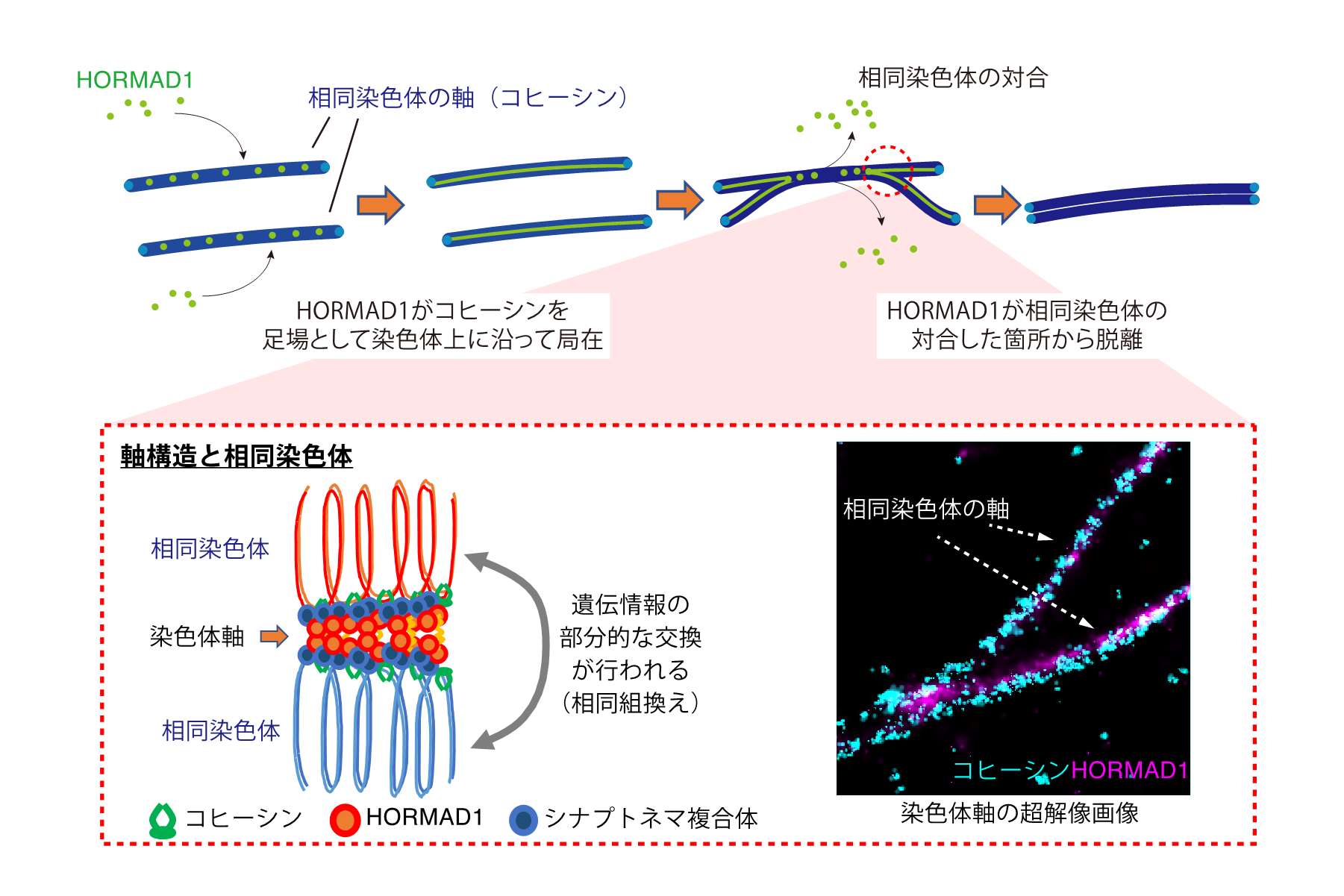
Epigenetics supports proper transmission of genetic information to progeny. Germ cells undergo dynamic morphological and molecular changes in order to transfer their genetic information to the progeny. For example, in sperm nuclei, which major axis is only 5 micrometer due to the histone removal and intense chromatin condenstaion, most of the nuclear events such as transcription and translation are thought to be shut-off. However, recent studies indicate that small amount of histones as well as RNAs still exist in mature sperm, and suggest the possibility that these histones and RNAs play some roles during fertilization. More recently, it is demonstranted that transient stress occurs in male individuals causes epigenetic alteration, and the altered epigenetic marks are inheritable to progeny. These observations support the idea that sperm transfer something other than their genome to the progeny.
In our laboratory, we focus on the chromatin dynamics in germ cells, and examine how it contributes cell proliferation, diff erentiation and fertilization, and three specific projects are on-going; i) identification and analysis of chromatin modifiers important for spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs), ii) investigating the roles of histone variants during spermatogenesis, and iii) profiling of histones retained in sperm and functional analysis of sperm histone variants.
Publication
- Solubilization of Mouse Sperm Chromatin for Sequencing Analyses Using a Chaperon Protein.
Fukuda Y, Shintomi K, Yamaguchi K, Fujiwara Y and Okada Y.
Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2577:161-173. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2724-2_11.
- Epigenetic regulator Cfp1 safeguards male meiotic progression by regulating meiotic gene expression.
Ki BS, Shim SH, Park C, Yoo H, La H, Lee OH, Kwon Y, Skalnik DG, Okada Y, Yoon HG, Kim JH, Hong K and Choi Y.
Exp Mol Med. 2022 Aug;54(8):1098-1108. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00813-0. Epub 2022 Aug 2.
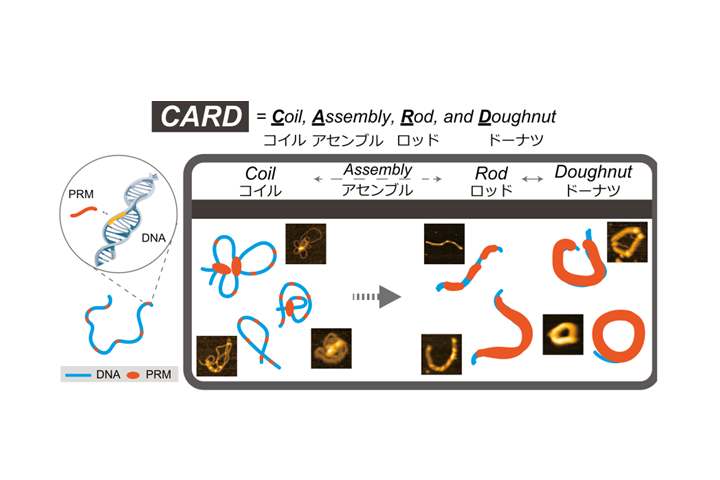
- Sperm chromatin condensation: epigenetic mechanisms to compact the genome and spatiotemporal regulation from inside and outside the nucleus.
Okada Y.
Genes Genet Syst. 2022 Jun 4;97(1):41-53. doi: 10.1266/ggs.21-00065. Epub 2022 Apr 29.
- Rubicon prevents autophagic degradation of GATA4 to promote Sertoli cell function.
Yamamuro T, Nakamura S, Yamano Y, Endo T, Yanagawa K, Tokumura A, Matsumura T, Kobayashi K, Mori H, Enokidani Y, Yoshida G, Imoto H, Kawabata T, Hamasaki M, Kuma A, Kuribayashi S, Takezawa K, Okada Y, Ozawa M, Fukuhara S, Shinohara T, Ikawa M and Yoshimori T.
PLoS Genet. 2021 Aug 5;17(8):e1009688. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009688. eCollection 2021 Aug.
- R-Loop Formation in Meiosis: Roles in Meiotic Transcription-Associated DNA Damage.
Fujiwara Y, Handel MA and Okada Y.
Epigenomes 2022, 6(3), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes6030026.
- Potential role of KRAB-ZFP binding and transcriptional states on DNA methylation of retroelements in human male germ cells.
Fukuda K, Makino Y, Kaneko S, Shimura C, Okada Y, Ichiyanagi K and Shinkai Y.
Elife. 2022 Mar 22;11:e76822. doi: 10.7554/eLife.76822.
- Sperm chromatin structure: insights from in vitro to in situ experiments.
Okada Y.
Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2022 Apr;75:102075. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2022.102075. Epub 2022 Mar 25.
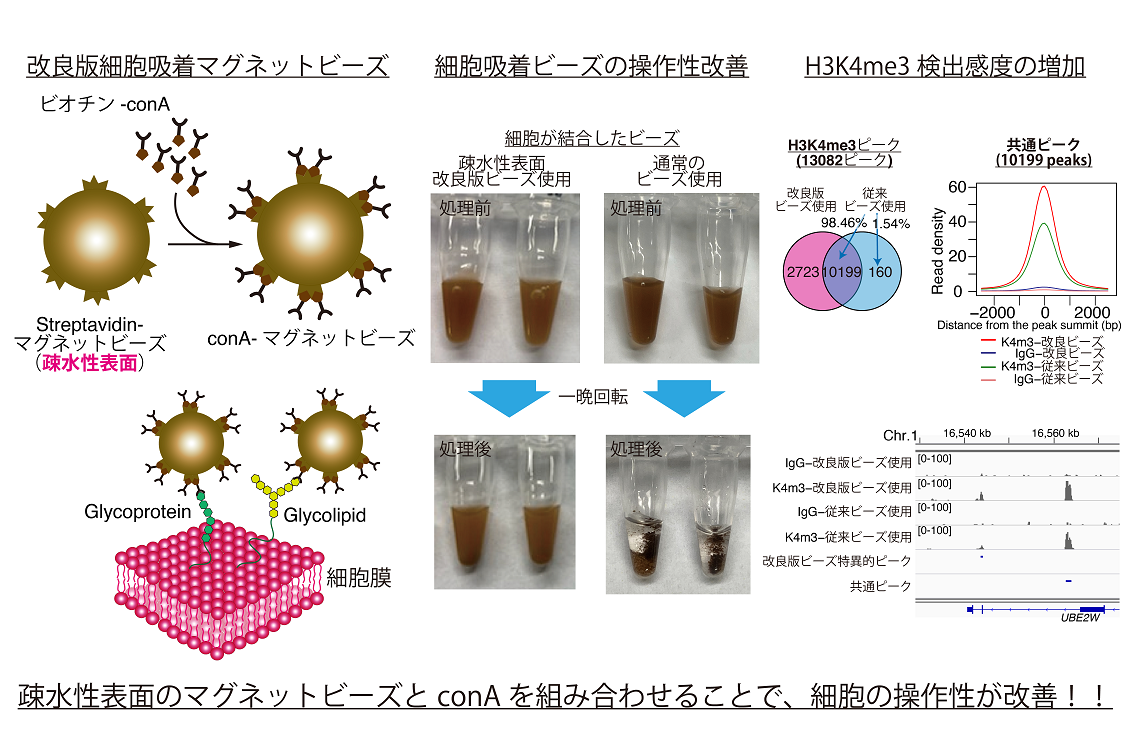
- Preparation of optimized concanavalin A-conjugated Dynabeads(R) magnetic beads for CUT&Tag.
Fujiwara Y, Tanno Y, Sugishita H, Kishi Y, Makino Y and Okada Y.
PLoS One. 2021 Nov 16;16(11):e0259846. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259846. eCollection 2021.
- Identification and characterization of the antigen recognized by the germ cell mAb TRA98 using a human comprehensive wet protein array.
Fukuda E, Tanaka H, Yamaguchi K, Takasaka M, Kawamura Y, Okuda H, Isotani A, Ikawa M, Shapiro VS, Tsuchida J, Okada Y, Tsujimura A, Miyagawa Y, Fukuhara S, Kawakami Y, Wada M, Nishimune Y and Goshima N.
Genes Cells. 2021 Mar;26(3):180-189. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12832.
- Protocol for isolation of spermatids from mouse testes.
Kim CR, Noda T, Okada Y, Ikawa M and Beek SH.
STAR Protoc. 2021 Jan 8;2(1):100254. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2020.100254. eCollection 2021 Mar 19.
Yuki Okada
Professor
Ph.D.
Pharmaceutical Sciences, Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
Yasuhiro Fujiwara
Research Associate
Ph.D.
Masashi Hada
Research Associate
Ph.D.
Erina Inoue
Technical Specialist
Ph.D.